Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board Assembly Guide
Table of contents
Table of contents
Introduction
The Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board is a key component of the LCC Fusion automation system, designed to control up to eight SG90 servo motors in model railroad applications and other low-power, precision movement tasks.
Working in conjunction with the LCC Fusion Node Card and PWM Card, this breakout board receives control signals over a standard network cable via the onboard PCA9685 PWM controller. Each servo motor connects directly using a standard 3-pin JST XH connector (Signal, 5V, GND), simplifying installation with RC-style servos such as the SG90.
The board is powered by the layout’s accessory power bus (AC or DC), which is routed through an onboard bridge rectifier and regulated down to 5V using a voltage regulator. This provides a stable power supply for all eight servo motors and the control circuitry. Output signals from the PCA9685 are buffered by an M54562FP Darlington array, ensuring reliable operation and electrical isolation.
Designed for seamless integration with other LCC Fusion components, the Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board enables accurate servo positioning for turnouts, semaphore signals, and animated scenic elements — all using a clean, modular wiring system.
flowchart LR;
subgraph layout ["Train Layout"];
n[["Node Card"]];
c[["PWM Card"]];
direction LR;
n --> c;
c --> bb[Servo Motor Driver <br/> Breakout Board];
bb --> m(("Servo Motors <br/> (x)"));
end;
classDef lSalmonStyle fill:#FFA07A,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,font-size:20px;
class bb lSalmonStyle;
classDef lightGrayStyle fill:#d3d3d3,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,font-size:24px;
class layout lightGrayStyle;
System Overview:
The Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board integrates seamlessly with the LCC Fusion Node Card and PWM Card to provide precise control over up to eight SG90 servo motors — a popular choice for turnout control, semaphore signals, and animated features in model railroad automation.
This system listens to the LCC CAN network and responds to LCC Events. These events trigger changes in servo position, such as moving a turnout from “closed” to “thrown,” based on preconfigured motion endpoints defined as percentages in the Node’s configuration.
Each servo is connected directly using a 3-pin JST XH connector (Signal, 5V, GND), while PWM control signals are generated by the PCA9685 PWM controller on the PWM Card. These signals are routed to the breakout board via a standard network cable. To ensure safe and consistent power, the breakout board accepts AC or DC accessory power, which is rectified and regulated to 5V for the servos.
Diagram Overview:
The diagram below illustrates the flow of control signals and power between the components in the Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board system:
- LCC Node Card: Receives LCC Events and manages configuration
- PWM Card: Generates PWM signals for servo control (via PCA9685)
- Breakout Board:
- Accepts 5V-regulated power from onboard AC/DC input
- Buffers control signals through M54562FP Darlington array
- Connects to up to 8 servos using 3-pin JST headers
flowchart LR
can["CAN Network"]
subgraph layout ["Train Layout"]
n["Node Card"]
c["PWM Card"]
direction LR
can --> |"LCC Event<br/>(Min/Max Position)"| n
n --> |"PWM Line Assignment"| c
c --> |"PWM Output<br/>(Pulse Width)"| bb[Servo Motor Driver<br/>Breakout Board]
bb --> |"Servo Control<br/>(5V PWM Signal)"| m["Servo Motors<br/>(8x SG90)"]
end
acc["AC or DCC<br/>Accessory Power"] --> |"Rectified & Regulated to 5V"| bb
classDef lSalmonStyle fill:#FFA07A,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,font-size:20px;
class bb lSalmonStyle;
classDef lightGrayStyle fill:#d3d3d3,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,font-size:24px;
class layout lightGrayStyle;
Control Flow:
- LCC Event:
- The system begins with an LCC Event sent over the CAN Network (e.g., a command to adjust the speed or change the direction of the Servo motors).
- Node Card:
- The Node Card receives this LCC Event and processes it, converting the event into GPIO input signals.
- PWM Card:
- The PWM Card, connected to the Node Card via a network cable, receives the GPIO input signals from the Node Card.
- The PWM Card, which uses the PCA9685 GPIO expander, converts these input signals into GPIO output signals.
- Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board:
- The Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board receives the GPIO output signals from the PWM Card through a network cable.
- The breakout board utilizes the M54562FP Darlington array to drive the Servo motors. This ensures efficient control of the motors by amplifying the signals and providing the necessary current.
- Powered by the 12 VDC layout accessory bus via the LM7812 voltage regulator, the breakout board provides stable power to both the control circuitry and the motors themselves.
- Servo Motor Operation:
- The breakout board then sends Servocontrol signals (e.g., step sequence, direction, and speed) to the Servo motors via simple JST XH 5-wire connectors.
- The system can control up to two 28BYJ-48 Servo motors, enabling a wide range of automated movements on the model railroad layout.
- Power:
- The breakout board and motors are powered by the layout accessory power bus (ACC POWER) through the LM7812, ensuring smooth and stable 12 VDC power supply for motor operations.
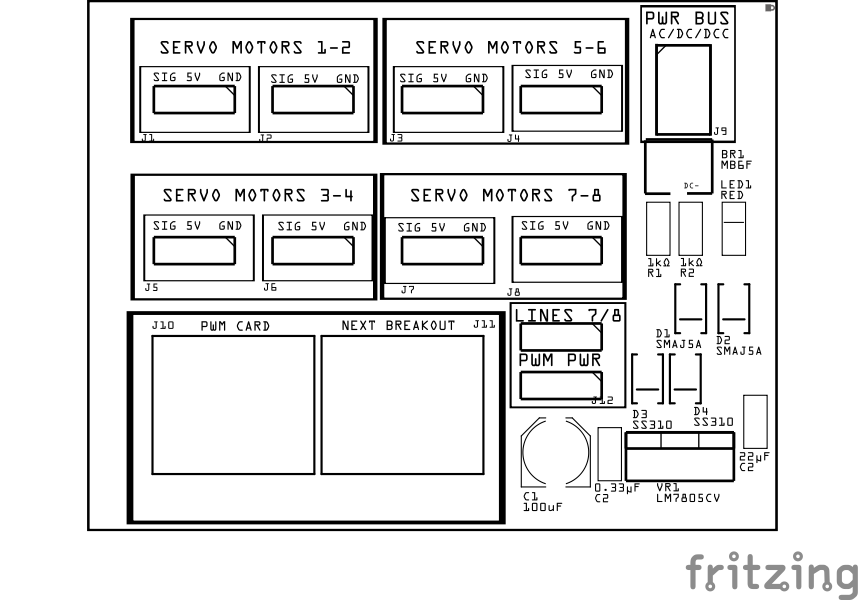
Assembly and Component Placement
This section combines both the component specifications and the assembly instructions to ensure a smooth assembly process. Below is a comprehensive list of components, their placement on the PCB, and orientation details to assist you during assembly.
High-Level Steps for Assembly:
- PCB for the card can be ordered from any PCB fabricator using these Gerber Files.
- Clean PCB with alcohol to remove residue. See Cleaning_PCB for details.
- See also: Soldering Tips
- PCB Components - listing of components used for PCB assembly
- PCB Parts - listing of parts used for PCB assembly
| Component Identifier | Count | Type | Value | Package | Purpose | Orientation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bridge Rectifiers | ||||||
| BR1 | 2 | Bridge Rectifier | MB6F | SOP-4 | Converts DCC pulsating AC-like waveform into a DC-like pulsating waveform for current detection. | Position IC’s indent to PCB bottom edge (pin1 DC-) |
| Capacitors | ||||||
| C1 | 1 | Capacitor-Polymer | 100 uF | 6.3x5.8mm SMD | Smooths rectified DC voltage | See silk screen image |
| C2 | 1 | Capacitor-Ceramic | 0.33µF | 1206 X7R | Used by 5V voltage regulator for input filtering. | None |
| C3 | 1 | Capacitor-Ceramic | 22 uF | 1206 X7R | Used by 5V voltage regulator for output filtering. | None |
| Diodes | ||||||
| D1 | 1 | TVS Diode | SMBJ18A | SMB | GPIO pin Transient Voltage Spike (TVS) protection | Cathode end has a white line and positioned towards PCB top edge |
| D1, D2 | 2 | TVS Diode | SMAJ5A | SMB SMD | Clamps voltage spikes on the 5 V line to protect logic and servos. | Cathode end has a white line and positioned towards PCB bottom edge |
| D3, D4 | 2 | Diode-Schottky | SS310 | SMD | Isolates power sources; allows higher voltage source to drive regulator. | Cathode end has a white line and positioned towards PCB bottom edge |
| D5, D6 | 2 | Diode-Schottky | SS310 | SMA | Required | Protects against reverse current |
| Connectors | ||||||
| J1 - J8 | 8 | Male Header | 3P, 2.54mm | n/a | Use to connect to servo motor SIG, 5V, GND | None |
| J9 | 1 | Connector | JST XH (2P) | 2.54mm | Connector to PWR BUS ground connection | Position connection towards PCB top edge |
| J10, J11 | 1 | RJ45 Socket | 8P8C | PTH | Network cable (CAT5/6) connection from PWM Card and to 2nd Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board | Fits only one way |
| Indicators | ||||||
| LED1 | 1 | LED | Red | 1206 SMD | Power indicator | Reference back of LED, position cathode towards PCB left edge |
| Resistors | ||||||
| R1 | 1 | Resistor | 1KΩ | PTH | Current limiting for power LED | None |
| R2 | 1 | Resistor | 1KΩ | PTH | Current limiting for Servo 7 signal (in case of mis-configured PWR GND) | None |
| Voltage Regulators | ||||||
| VR1 | 1 | Voltage Regulator | LM7805CV | TO-220 SMD | Provides 5V to Servo Motors | Position heat sink towards PCB top edge |
Tools Required
Safety Precautions
- See Safety Precautions.
Testing and Verification
Visual Inspection
- Initial Check: Examine the board for any obvious issues like missing components, solder bridges, or components that are misaligned or not fully seated.
- Solder Joint Inspection: Use a magnifying glass or a microscope to inspect solder joints. Look for cold solder joints, insufficient or excessive solder, or any shorts between pads.
Functional Testing
Troubleshooting
- See I2C Trouble Shooting.
Appendences
PCB Specifications
Specifications for the Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board include:
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Max Motors | 8 |
| Output | 5V |
| Max Output1 | 1.5A |
| Maximum Number of Servo Motor Driver Breakout Boards per PWM Card | 2 |
- Max current across all servo motors is based on the LM7805 voltage regulator and fuse.
How It Works
-
LCC Events Drive Servo Control via ESP32 and PCA9685:
-
The ESP32-based Node Card listens for LCC Events over the CAN network. These events are typically triggered by layout automation (e.g., button presses, occupancy sensors).
-
When a relevant event is received, the Node sends a command to the PWM Card, which uses the PCA9685 to generate a precise PWM signal for each connected servo.
-
Each PWM signal encodes a specific servo position by adjusting the pulse width (typically between 1 ms and 2 ms for SG90 servos).
-
-
PWM Card Outputs Routed to the Breakout Board:
-
The PWM Card connects to the Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board via a standard network cable (e.g., CAT5/6).
-
This cable carries up to 8 PWM signals (one per servo), along with power and ground, simplifying wiring and making it easy to distribute signals across a layout.
-
-
Power Input and Regulation for Servos:
-
The breakout board accepts AC or DC accessory power from the layout’s bus.
-
This input is routed through a bridge rectifier, then regulated to a stable 5V using an onboard voltage regulator (e.g., LM7805 or similar).
-
The regulated 5V supply powers the SG90 servo motors, which require clean voltage to avoid jitter or reset behavior during movement.
-
-
Direct Servo Connection Using 3-Pin JST Headers:
-
Each SG90 servo is connected using a standard 3-pin JST XH connector (Signal, 5V, GND).
-
The PWM signal controls the servo angle, which is configured as a min/max percentage in the Node’s CDI settings (e.g., 0% for closed, 100% for thrown)
-
PCB Protection
The Servo Motor Driver Breakout Board includes several key protection mechanisms to safeguard both the board itself and the connected components. Below is a detailed table outlining the protection provided against flyback voltage and reverse voltage, ensuring the longevity and reliability of your setup.
| Protected Component | Protection Component | Function | Specifications | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 V Regulator & Servo Power Supply | Bridge Rectifier | Ensures correct polarity and allows AC, DC, or DCC power while blocking reverse input. | - Max Input Voltage: 600 V AC- Avg Forward Current: ≥1 A- Vf: ~1.1 V per diode | Between accessory PWR BUS and regulator input |
| **5 V Regulator Output ** | TVS Diode (SMAJ5A) | Clamps voltage spikes on the 5 V line to protect logic and servos. | - Breakdown: ~6.4 V- Clamping: ~9 V- Unidirectional | Across 5 V rail and GND (after regulator output) |
| Dual 5 VDC Sources (Line 7 vs. Local Regulator) | Schottky Diodes (D6–D7, SS310) | Prevents back feeding between LCC card’s 5 VDC (Line 7) and local 5 VDC regulator | Vf ≈ 0.3–0.4 VDC @ 100 mA, 1–3 A IF, 40–100 VDC VR | Anode from each 5 VDC source, cathodes tied together to breakout +5 VDC rail |
| LM7805 Regulator | Input/Output Capacitors | Stabilizes voltage and suppresses regulator oscillation and ripple. | - Input: 0.33 µF + 220 µF- Output: 0.1 µF + 220 µF | Close to regulator pins: IN ↔ GND, OUT ↔ GND |
| Regulator Input Selector (Lines 7/8 vs. PWR BUS) | SS310 Diodes (x2) | Isolates power sources; allows higher voltage source to drive regulator. | - Forward current: 3 A- Vf: ~0.45 V- Reverse voltage: 100 V | One from Line 8 → VREG_IN, one from PWR BUS → VREG_IN |
| Servo Signal Input (PWM Mode Only)1 | 1k Resistor + SMAJ5A TVS | Protects servo from overvoltage if Line 8 is misconfigured as 12 V. | - Resistor: 1kΩ current-limiting- TVS: SMAJ5.0A (clamps ~6.4 V) | Between Line 8 and servo signal pin (only when Line 8 = PWM) |
- Line 7 cannot be configured as a power source (5 V or 12 V). It is limited to either GND or a 3.3 V PWM signal by the PWM Card’s selector. Therefore, overvoltage protection (TVS/resistor) is not necessary on this line.